Code emulation with Ghidra SRE
Written by Jiří Keresteš on 2021-04-08
pythonDid you know that Ghidra SRE has the ability to emulate code? If you want to know how we use it to save time when reversing firmware binaries, read on!
Ghidra can emulate instructions, although not directly from GUI. You'll need to use Ghidra scripting API. Fortunately, the documentation is rather good and the whole process is rather straightforward. In this article, we'll focus on using Ghidra API from a Jupyter Notebook with Kotlin kernel.
First, we need to install Ghidra-Jupyter kernel. We
should be able to see Ghidra(Kotlin) kernel in our Jupyter lab
interface.

If the kernel is missing, Jupyter can't find our freshly-installed
kernel.json kernelspec. Use jupyter kernelspec install
command to set the correct path.
Open a new Jupyter notebook with Ghidra(Kotlin) kernel. Then in Ghidra CodeBrowser, click the Kotlin Notebook button

Ghidra extension will connect to the running Jupyter kernel. Now we have a fully
synchronized Jupyter notebook for Ghidra! This means we can access objects like
currentProgram or currentAddress exactly like in Ghidra
scripting console.
Let's look at the emulation capabilities we promised. ghidra.app.emulator.EmulatorHelper
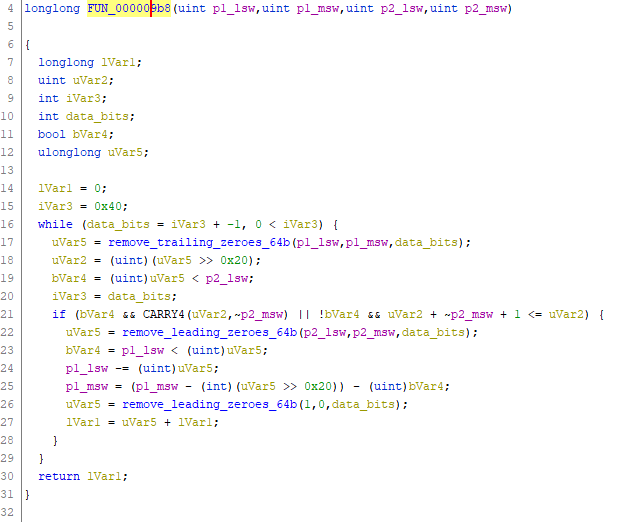
class does the heavy lifting for us. In this example, our target will be a partially
analyzed function:
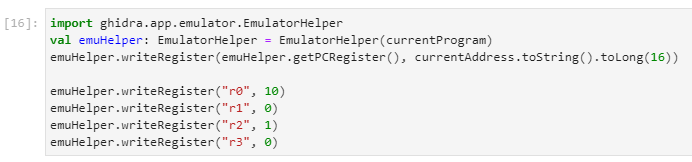
We've previously figured out parameter types and meaning, but what is the returned value? Let's set up the initial emulator state.
Then we step through the code until we reach the function return address.
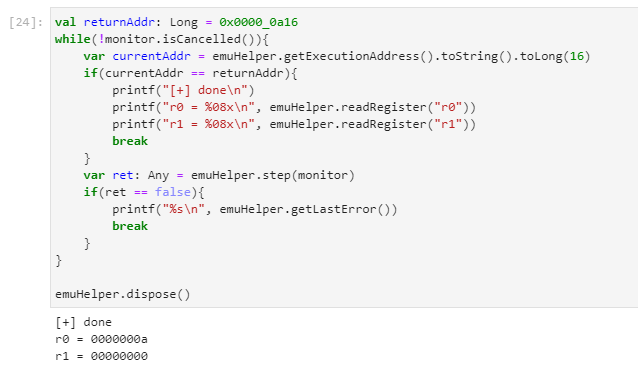
Playing around with input parameters we figure out that our specimen function is an integer division of two 64-bit values. This approach can be very useful when trying to wrap your head around a piece of code with a lot of binary twiddling.
Happy reversing!
